M270 PFAS Treatment for Industrial Water Systems
Innovative PFAS Therapy Solutions for Safer Water
The enhancing frequency of PFAS contamination in water materials demands an essential exam of ingenious therapy services. Advanced purification innovations and unique chemical treatments existing encouraging opportunities for lowering these consistent toxins. Additionally, arising bioremediation techniques supply a more lasting method to taking on PFAS challenges. As regulative structures remain to adapt, recognizing the efficiency and scalability of these remedies becomes vital. What effects do these developments hold for public health and wellness and ecological reconstruction, and how can stakeholders efficiently apply them in varied contexts?
Review of PFAS Contamination
PFAS contamination has actually emerged as a significant environmental and public wellness issue. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a group of synthetic chemicals understood for their perseverance in the atmosphere and body, leading them to be frequently described as "forever chemicals." These compounds have been widely made use of in various markets, including firefighting foams, water-repellent fabrics, and food product packaging, mostly because of their water- and grease-resistant properties.
The extensive use PFAS has caused their detection in soil, water supplies, and also in the blood of humans and animals. Researches have connected PFAS exposure to many health concerns, consisting of developmental impacts in babies, body immune system dysfunction, and numerous types of cancer cells. Additionally, the ecological determination of these substances complicates their degradation and removal, elevating concerns about long-term eco-friendly impacts.
Regulatory bodies are significantly executing strict guidelines to keep track of and decrease PFAS levels in drinking water and other ecological mediums. As awareness of PFAS contamination grows, it has come to be important for communities and industries to seek effective therapy services to alleviate direct exposure and safeguard public wellness.
Advanced Purification Technologies
As the seriousness to address PFAS contamination heightens, advanced filtration innovations have become a critical part in the removal efforts focused on getting rid of these relentless chemicals from water resources. These innovations take advantage of advanced devices to effectively target and capture PFAS substances, which are notoriously immune to standard treatment techniques.
One of the most appealing methods is making use of granular turned on carbon (GAC), which adsorbs PFAS molecules because of its high surface and permeable structure. This approach has been commonly applied in both community and commercial setups, showing considerable decreases in PFAS focus. Additionally, ion exchange materials have actually acquired traction, particularly developed to uniquely bind PFAS ions from water, therefore promoting their removal.
Membrane layer filtering innovations, such as reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, also reveal effectiveness in PFAS removal by physically separating contaminants from water - pfas management. These systems can attain high degrees of purity, making them ideal for drinking water applications
Chemical Therapy Innovations
Various chemical treatment developments are being checked out to properly address PFAS contamination in water materials. One promising approach includes the usage of sophisticated oxidation procedures (AOPs), which make use of effective oxidants such as ozone, hydrogen peroxide, or chlorine dioxide combined with UV light to damage down PFAS substances into less dangerous materials. This approach has demonstrated efficacy in laboratory settings, revealing possible for scalability in real-world applications.
One more ingenious method is the advancement of ion-exchange resins specifically made to target PFAS. These materials can uniquely adsorb PFAS compounds from water, enabling their removal during treatment processes. Recent advancements have actually boosted the effectiveness and capacity of these resins, making them a favorable option for water treatment centers.
Additionally, scientists are try this website investigating the use of chemical representatives like persulfate and ferrous ions to boost the destruction of PFAS in contaminated water. These representatives can generate chemical reactions that assist in the malfunction of consistent PFAS substances.
Arising Bioremediation Methods
Recent advancements in chemical therapy innovations have actually paved the way for exploring bioremediation techniques as a sensible choice for addressing PFAS contamination. Bioremediation takes advantage of the natural metabolic processes of microbes to weaken or change pollutants, making it an appealing approach for taking on relentless pollutants like PFAS.
Emerging techniques in bioremediation consist of using genetically crafted microbes that can specifically target and damage down PFAS compounds. These microbial stress are being created for their boosted destruction capacities, increasing the performance of the removal process. Furthermore, researchers are investigating the potential of plant-assisted bioremediation, where particular plant varieties might uptake and sequester PFAS from polluted soil and water.
An additional appealing approach is the application of bioaugmentation, which entails introducing helpful microorganisms right into polluted environments to increase the deterioration of PFAS. This technique can promote quicker remediation timelines and boost general efficiency.

Regulatory Frameworks and Criteria
A detailed governing structure is vital for efficiently taking care of PFAS contamination and making certain public wellness security. The raising recognition of per- and polyfluoroalkyl materials (PFAS) as toxic wastes has actually motivated various government and state agencies to develop standards that regulate their existence in water supplies. The U.S. Environmental Defense Company (EPA) has developed health and wellness advisories and is pursuing setting enforceable limitations for PFAS in drinking water.
State-level policies vary considerably, with some states embracing more stringent guidelines than those recommended by the EPA. These guidelines typically include optimum pollutant levels (MCLs) for specific PFAS substances, surveillance demands, and reporting responsibilities for water utilities. Additionally, arising frameworks concentrate on the remediation of contaminated sites, emphasizing the need for efficient treatment innovations.
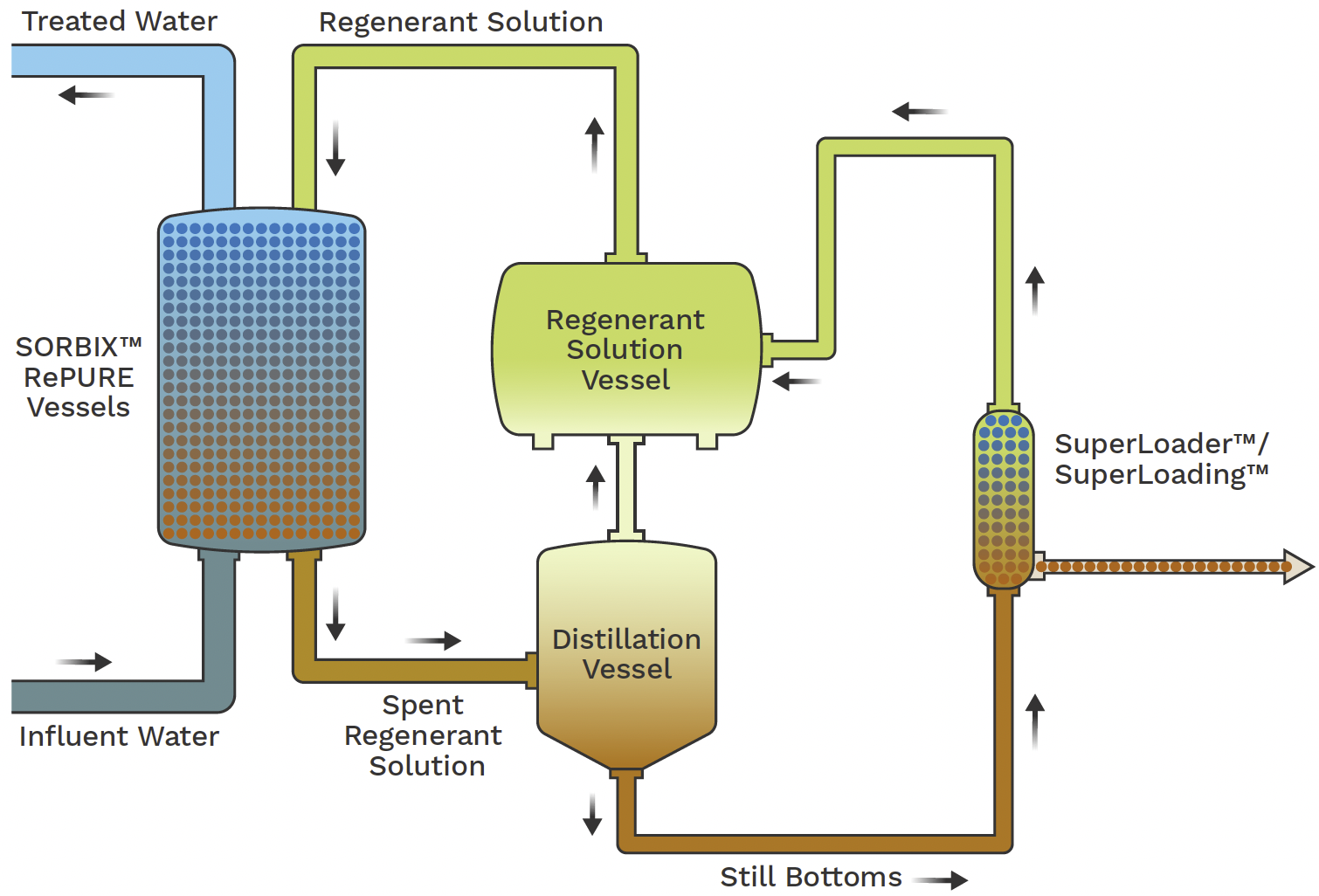
Conclusion
In final thought, the advancement and application of innovative PFAS treatment services are important for resolving the pervasive issue of water contamination. Advanced filtering technologies, chemical treatments, and arising bioremediation techniques collectively offer a diverse strategy to successfully lower and weaken PFAS degrees. As governing structures continue to progress, incorporating these modern technologies will be necessary to protect public health and wellness and bring back the stability of contaminated water resources, inevitably adding to a cleaner and safer atmosphere.